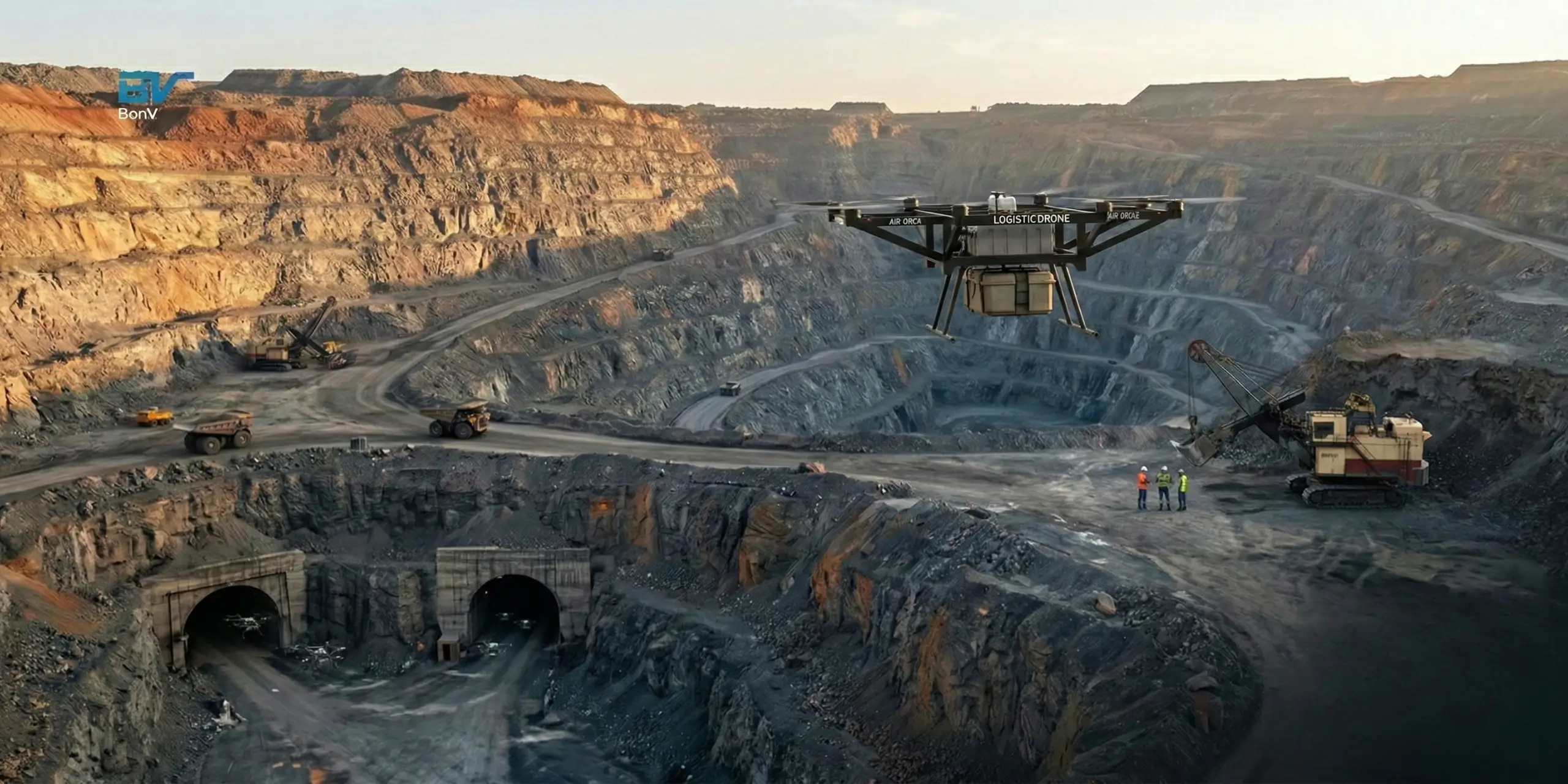
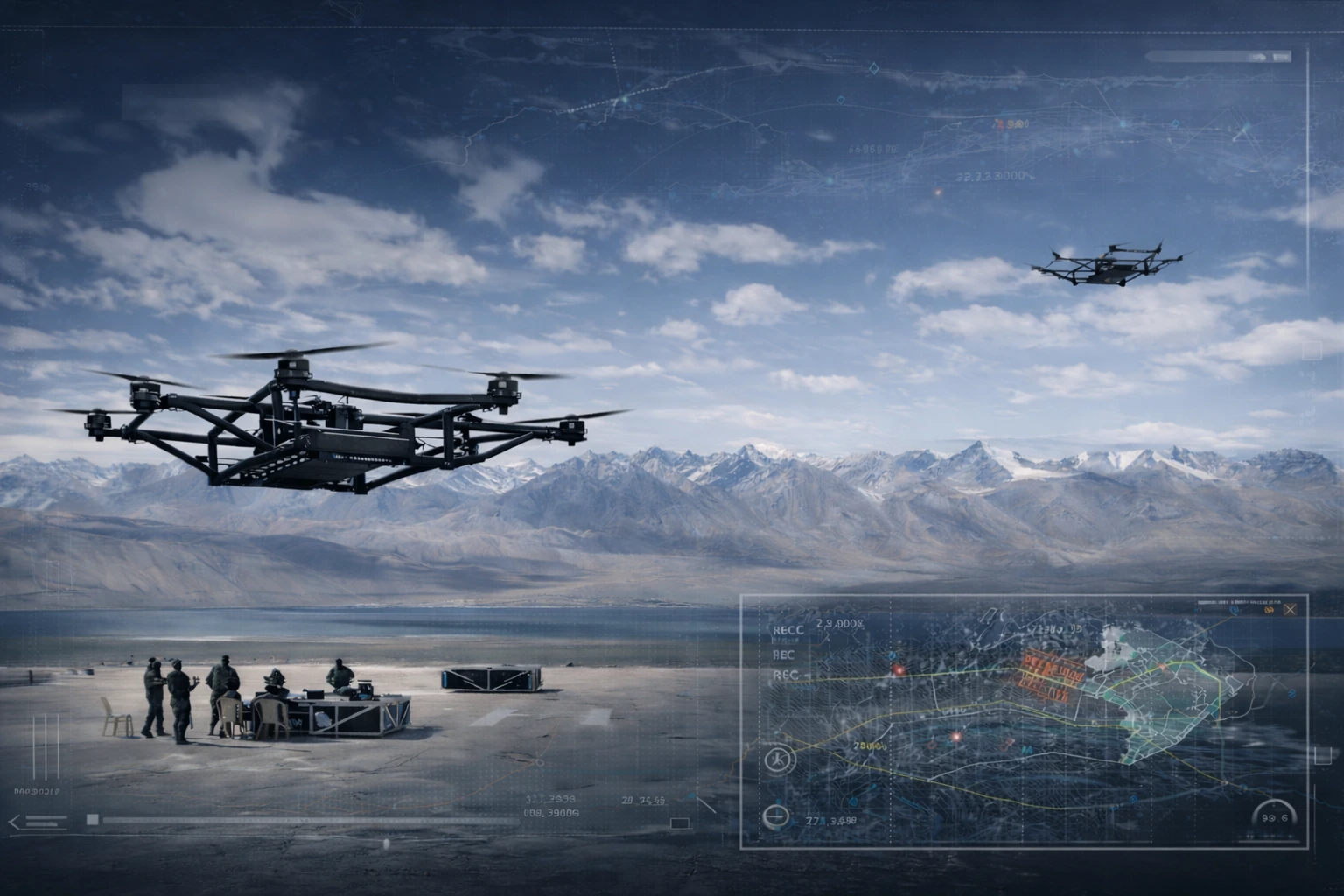
Traditionally, mining has been a difficult and demanding profession. On a typical site, a small missing spare part can stop heavy machinery for hours. In underground mines, delivering urgent tools or medical supplies can mean sending workers through narrow, potentially risky tunnels. Delays cost money and safety risks cost even more.
This is exactly why the logistics drone in mining is becoming so important. Instead of relying only on ground vehicles, operators can now use aerial systems to deliver supplies quickly and safely. As mines grow larger and more automated, drone logistics for mining operations is no longer experimental; it’s a practical step towards smarter, safer mine sites.
According to Future Market Report the mining drone service market was valued around USD 1,750 million in 2025 and is expected to grow to over USD 4,510 million by 2032, signaling increasing use of drone-based services in safety, monitoring and logistics tasks.
What Is a Logistic Drone in Mining?
In modern mining operations, not every drone is built for surveying or mapping. Some are specifically engineered to carry physical loads, moving tools, spare parts, samples, medical kits and other essential supplies from one point to another across a mining site.
Unlike standard survey drones, these aircraft are designed with a strong focus on payload capacity, flight stability and reliable navigation in harsh environments. Whether operating above a large open pit or inside confined underground tunnels, they must remain steady, precise and dependable.
An industrial logistics drone used in mining typically includes:
- Heavy payload capacity (from around 2 kg up to 50+ kg, depending on the model)
- Autonomous navigation systems for pre-programmed routes
- Advanced obstacle avoidance sensors
- Encrypted communication systems for secure operations
- A rugged design built to withstand dust, strong winds and extreme temperatures
These drones act as airborne supply carriers. By reducing dependence on ground vehicles in difficult terrain, they help mining operations move essential items faster, safer and more efficiently.
10 Key Applications of Logistic Drones in Mining Operations
1. Transporting Critical Supplies
In large open-pit mines, distances can be massive. Moving a small tool or spare part from one end of the site to another may involve long vehicle routes, fuel usage and significant waiting time.
A UAV for mining logistics can complete the same task in minutes by flying directly to the required location. Instead of shutting down equipment while waiting for a component, operators receive fast aerial delivery improving uptime, productivity and overall operational flow.
2. Underground Mine Delivery
One of the most impactful uses of drone logistics for mining operations is underground. Underground environments bring several challenges:
- Narrow tunnels
- Limited visibility
- Ventilation constraints
- Increased safety risks for personnel
An autonomous system designed for underground use can follow predefined routes, avoid obstacles and deliver equipment without sending workers into potentially hazardous zones.
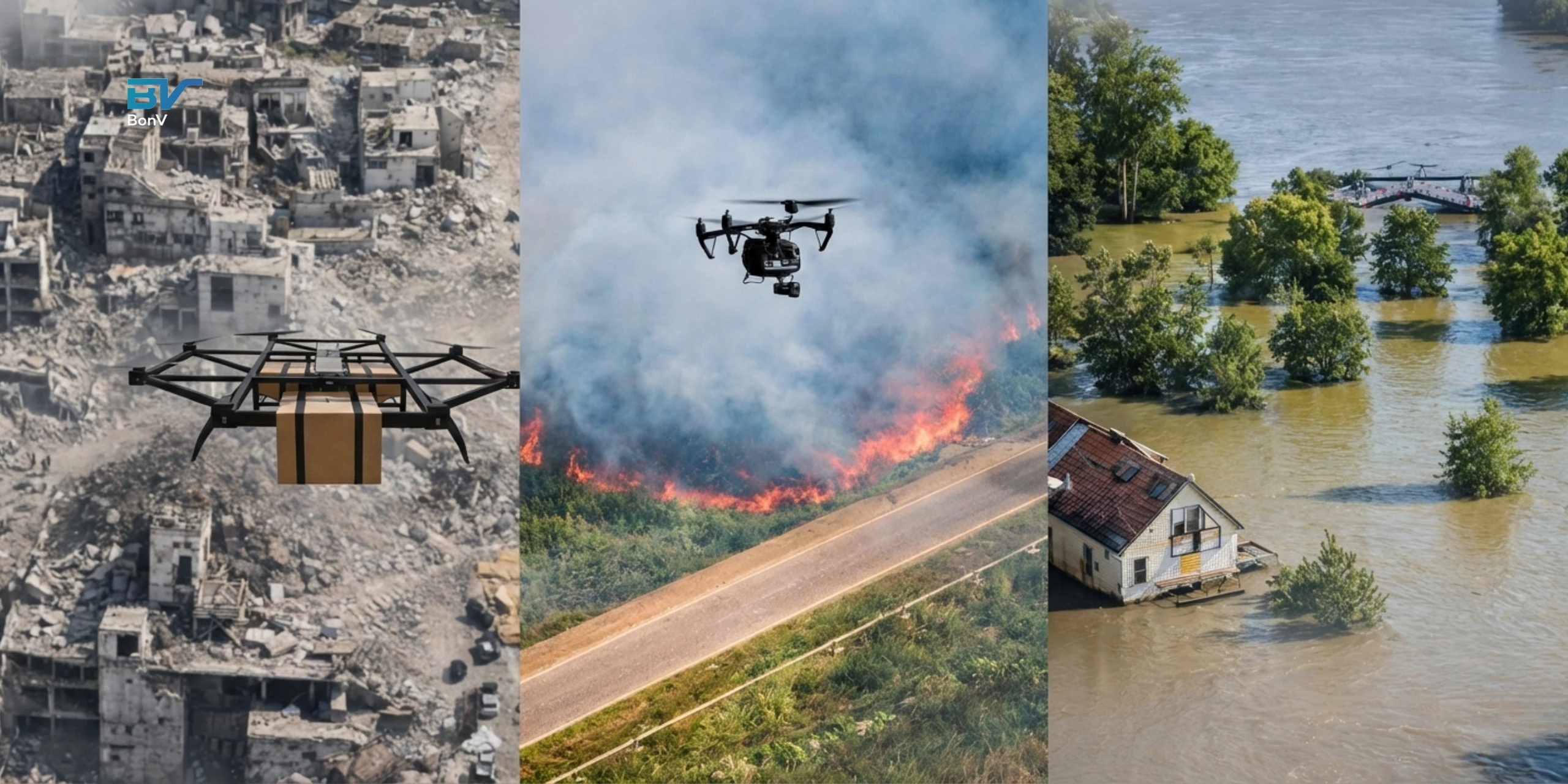
3. Emergency & Rescue Support
In mining, emergency response time can make a critical difference. Delivering medical kits, communication devices or gas detection sensors quickly is essential.
An industrial logistics drone can be deployed immediately, even before rescue teams enter uncertain conditions. In underground operations, this capability enhances response speed and strengthens overall safety protocols.
4. Sample & Material Transfer
Transporting geological samples efficiently is vital for analysis and decision-making. Delays in moving samples can slow down operational planning.
By using a UAV for mining logistics, samples can be transferred quickly and securely from extraction points to testing facilities. Reduced manual handling not only saves time but also supports faster analysis enabling more informed and timely decisions on-site.
5. Delivery of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
On large mining sites, situations can change quickly. A worker may suddenly need a replacement respirator, safety lamp or other protective gear.
Instead of leaving the work zone and travelling back to a storage area losing valuable time, aerial delivery systems can transport essential PPE directly to the required location. This helps maintain safety compliance while keeping operations running smoothly.
6. Tool Dispatch for Maintenance Teams
Maintenance teams are often spread across different sections of a mine. If a specific tool is missing, even a minor delay can interrupt planned repairs and extend equipment downtime.
With drone logistics for mining operations, required tools can be sent directly to technicians in the field. Faster delivery supports quicker repairs and ensures that heavy machinery returns to operation without unnecessary disruption.
7. Remote Site Support in Exploration Projects
Exploration projects are frequently based in remote or rugged terrain where infrastructure is limited. Ground vehicles may take considerable time to navigate rough access routes.
In these conditions, a UAV for mining logistics can move smaller equipment, batteries, sensors or documentation efficiently over short to medium distances. This improves responsiveness without increasing vehicle dependency.
8. Inventory Movement Between Storage Points
Large mining operations often manage multiple storage facilities across the site. Moving lightweight parts or consumables between these locations can involve repeated vehicle trips.
Using aerial transport for small inventory transfers helps streamline internal supply chains and reduces pressure on vehicle fleets, particularly during peak operational hours.
9. Environmental Monitoring Equipment Deployment
Environmental monitoring is an essential part of modern mining. Installing or replacing air quality sensors, dust monitors or gas detection devices in elevated or hard-to-reach areas can be labour-intensive.
Aerial systems can safely transport and position lightweight monitoring equipment, especially in locations where access is restricted or conditions are challenging.
10. Support During Shift Changes
During shift transitions, teams may need to exchange documents, storage devices or small tools between different operational zones. Even short delays can slow down handovers.
Mining drones can manage these short-distance transfers efficiently, supporting smoother shift changes and maintaining operational continuity across teams.
While these examples focus on mining, the broader logistic drone use cases span multiple industries including construction, healthcare, defence and infrastructure.
5 Benefits of Using Logistic Drones in Mining
The advantages of adopting drones in mining go beyond simple transportation. From underground environments to large open-pit sites, the impact is both operational and strategic.
- Improved Safety: Safety is always the top priority. By using a mining drone to transport tools, spare parts or emergency supplies, companies can reduce the need for workers to enter unstable zones, active haul routes or post-blast areas. Fewer vehicle movements and less human exposure directly contribute to lower accident risks.
- Faster Delivery: Mining sites often cover vast areas, and ground transport can be slow due to rough terrain and heavy equipment traffic. A mining drone takes a direct aerial route, bypassing obstacles and congestion. The result is significantly faster delivery times and smoother daily operations.
- Lower Operational Costs: Reducing reliance on fuel-powered vehicles lowers fuel consumption, maintenance expenses and overall fleet wear. Over time, integrating drone logistics into site operations can improve cost efficiency and optimise resource use.
- Reduced Downtime: Equipment downtime can quickly impact production targets. When critical components are delivered rapidly using a logistics drone in mining, machinery can return to operation sooner protecting output and revenue.
- Better Data Visibility and Integration: Modern drone platforms are connected systems. A mining drone can integrate with site management software, allowing real-time tracking, route planning and operational insights. This supports data-driven decision-making and strengthens overall logistics control.
For mining companies embracing automation and digital transformation, adopting mining drone technology goes beyond faster deliveries. It helps improve safety, strengthen operational control, and create a more connected and efficient mine ready for the future.
Underground vs Open-Pit Mining Drone Logistics
Drone operations in mining vary significantly depending on the environment. Open-pit and underground mines have very different logistical demands, so the technology must be adapted to suit each setting.
1. Open-Pit Mining
Open-pit sites usually involve long distances, exposure to wind and changing weather, and larger operational zones. In these conditions, drones are designed for:
- Longer flight range
- Higher payload capacity
- Stable performance in outdoor environments
- GPS-supported navigation
The focus here is on endurance, strength and the ability to cover wide areas efficiently.
2. Underground Mining
Underground mines are more complex and confined. They operate in GPS-denied environments with narrow tunnels and limited visibility. In these settings, drones rely on:
- LiDAR and SLAM-based navigation
- Advanced obstacle detection
- Compact and agile designs
- High-precision autonomous control
Drone logistics for mining operations must match the mine’s structure. Underground systems prioritise navigation accuracy and safety, while open-pit systems emphasise range, payload and environmental durability.
Technology Behind Mining Logistic Drones
A mining drone is powered by a mix of smart software and robust hardware designed to handle tough site conditions. It’s not just about flying, it’s about flying safely, accurately and reliably in complex environments.
Most industrial logistics drone systems include:
- Autonomous flight control for stable, pre-planned routes
- AI-based obstacle detection to avoid collisions
- LiDAR for underground mapping and positioning
- RTK systems for precise surface navigation
- Secure, encrypted communication links
- Battery optimisation for better flight endurance
In underground mines, where GPS doesn’t work, drones rely on SLAM (Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping). This allows them to map tunnels in real time while tracking their own position, ensuring safe and accurate movement.
Together, these technologies make a UAV for mining logistics a practical and dependable solution for modern mining operations.
Challenges of Implementing Logistic Drones in Mining
While the benefits are clear, adopting a logistics drone in mining also comes with practical challenges. Like any new technology, successful implementation requires planning, testing and adaptation to site conditions.
- Harsh Operating Environments: Mining sites are demanding. Dust, vibration, moisture and extreme temperatures can affect drone performance. Equipment must be rugged, well-protected and regularly maintained to ensure reliability.
- Battery Limitations: Payload weight directly impacts flight time. In underground operations especially, limited charging access can restrict continuous deployment. Planning charging stations or battery swap systems becomes essential.
- Regulatory and Safety Approvals: Depending on the region, aviation authorities may require permissions for drone operations, particularly for beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) flights. Mines must also integrate drone use into their internal safety protocols.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Drone logistics should not operate in isolation. For maximum efficiency, it must integrate with mine management software, inventory systems and operational workflows. Without proper integration, the full value cannot be realised.
- Workforce Training and Acceptance: Introducing new technology requires training teams and building confidence in the system. Operators, maintenance crews and safety managers must understand how the drone fits into daily operations.
Despite these challenges, the technology is rapidly maturing. With proper planning and infrastructure, drone logistics for mining operations can be implemented in a way that delivers long-term efficiency, safety and operational gains.
Future of Autonomous Drone Logistics in Mining
The future of mining drone technology is clearly moving towards greater autonomy and smarter integration. What is being used today for basic deliveries could soon become a fully automated logistics network within the mine.
In the coming years, drones are expected to connect directly with inventory systems and maintenance software. For example, if a machine reports a fault or stock runs low, a delivery could be triggered automatically without manual coordination.
We’re also likely to see automated charging stations, improved battery performance and more advanced AI-based route planning. As automation expands across the mining sector, logistics drones in mining operations will shift from being a support tool to becoming a core part of everyday site efficiency.
As this evolution continues, autonomous drone logistics will play a central role in creating mining operations that are safer, faster and seamlessly connected.
The Shift Towards Autonomous Mining Logistics
Mining is changing. It’s no longer only about extracting resources, it’s about how safely, efficiently and intelligently a site operates every single day. As mines grow larger and more automated, internal logistics needs to evolve as well.
It’s not just a technological upgrade; it’s a practical solution to real operational challenges. Faster deliveries, reduced downtime and improved worker safety all contribute to a more reliable and productive working environment. As more companies adopt advanced aerial systems, it’s clear that this technology is becoming an integral part of modern mine infrastructure.
At BonV Aero, we are a logistics drone manufacturing company in India, building industrial-grade aerial systems designed for demanding environments such as mining. With capabilities in heavy-payload drone design, autonomous flight systems and customised enterprise integration, our aim is simple to support safer operations, smoother logistics and a smarter future for the mining industry.

Umang Kumar Rathi is Co-Founder and COO of BonV Technology. With 12+ years of experience and a background in aerospace and strategy, he brings a sharp product mindset and system thinking to building reliable and scalable eVTOL solutions.